<--- Back to Details
| First Page | Document Content | |
|---|---|---|
 Date: 2012-03-21 13:03:11Chemistry Halomethanes Ozone depletion Environment Temperature Chiller Dichlorodifluoromethane Air conditioning 1 1 2-Trichloro-1 2 2-trifluoroethane Refrigerants Chlorofluorocarbons Heating ventilating and air conditioning |
Add to Reading List |
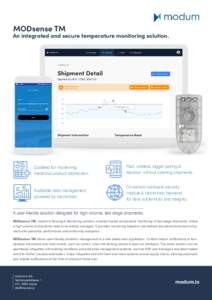
 Buildings Energy Data Book: 5.3 Heating, Cooling, and Ventilation EquipmentPre
Buildings Energy Data Book: 5.3 Heating, Cooling, and Ventilation EquipmentPre