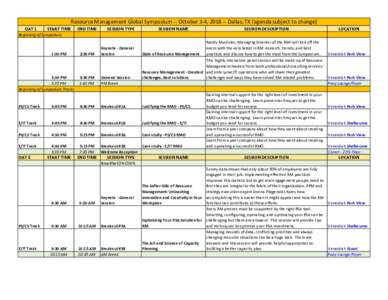
<--- Back to Details
| First Page | Document Content | |
|---|---|---|
 Date: 2013-05-29 04:09:08Sustainability Environmentalism Sustainability science International Human Dimensions Programme Global change Environmental governance Planetary boundaries Sustainable development Earth System Science Partnership Environment Earth Environmental social science |
Add to Reading List |
 POLICYFORUM ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT Earth System Science for Global Sustainability: Grand Challenges
POLICYFORUM ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT Earth System Science for Global Sustainability: Grand Challenges