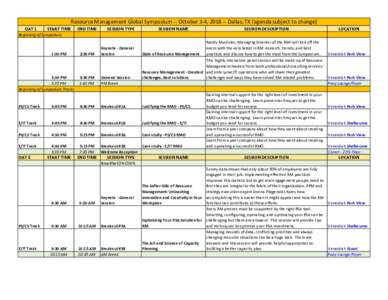
<--- Back to Details
| First Page | Document Content | |
|---|---|---|
 Date: 2013-08-12 05:54:22Sustainability Global change Sustainable development Sustainability science International Human Dimensions Programme Environment Environmental social science Earth |
Add to Reading List |
 Joint Statement – Belmont Forum, ICSU and ISSC
Joint Statement – Belmont Forum, ICSU and ISSC