<--- Back to Details
| First Page | Document Content | |
|---|---|---|
 Date: 2013-05-10 13:24:23Spaceflight Gold panning Gravel Sand Opportunity rover Sediment Panning Sedimentology Geology Spacecraft |
Add to Reading List |
 | Experience with Rule-Based Analysis of Spacecraft Logs? Klaus Havelund and Rajeev Joshi Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology California, USADocID: 1xUdS - View Document |
 | Comprehension of spacecraft telemetry using hierarchical specifications of behavior? Klaus Havelund and Rajeev Joshi Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology California, USADocID: 1xTRi - View Document |
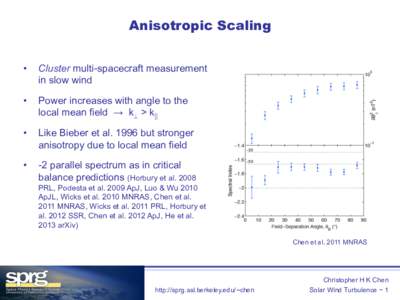 | Anisotropic Scaling • Cluster multi-spacecraft measurement in slow windDocID: 1vojz - View Document |
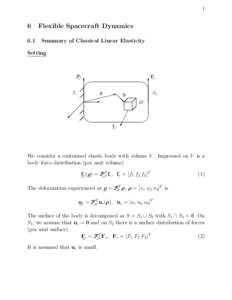 | Flexible Spacecraft DynamicsDocID: 1uO4J - View Document |
![Resolving Spacecraft Earth-Flyby Anomalies with Measured Light Speed Anisotropy Reginald T. Cahill arXiv:0804.0039v3 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Apr 2008 Resolving Spacecraft Earth-Flyby Anomalies with Measured Light Speed Anisotropy Reginald T. Cahill arXiv:0804.0039v3 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Apr 2008](https://www.pdfsearch.io/img/6ce6d6971109dc421cc8bd20744ee110.jpg) | Resolving Spacecraft Earth-Flyby Anomalies with Measured Light Speed Anisotropy Reginald T. Cahill arXiv:0804.0039v3 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Apr 2008DocID: 1uFIe - View Document |
 Figure 3. Increase in tilt should be smooth and continuous, not jerky. Stop when the edge of the sand and gravel reaches the rim of the pan (see Figure 3). With the pan in the last position shown in Fig. 3, gently immer
Figure 3. Increase in tilt should be smooth and continuous, not jerky. Stop when the edge of the sand and gravel reaches the rim of the pan (see Figure 3). With the pan in the last position shown in Fig. 3, gently immer