<--- Back to Details
| First Page | Document Content | |
|---|---|---|
 Date: 2011-09-10 15:21:30Matrix Nitric acid Internal standard Graphite furnace atomic absorption Detection limit Standard addition Sample preparation in mass spectrometry Ion source Atomic absorption spectroscopy Chemistry Analytical chemistry Calibration curve |
Add to Reading List |
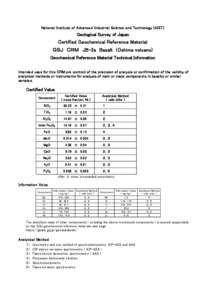
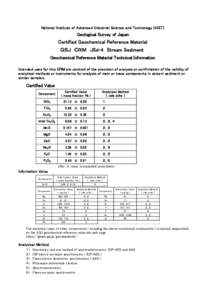
 Method[removed]Determination of Trace Elements in Marine Waters by Off-Line Chelation Preconcentration with Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption John T. Creed and Theodore D. Martin Inorganic Chemistry Branch
Method[removed]Determination of Trace Elements in Marine Waters by Off-Line Chelation Preconcentration with Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption John T. Creed and Theodore D. Martin Inorganic Chemistry Branch