1 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: genepath.med.harvard.eduLanguage: English - Date: 2017-10-11 15:45:23
|
|---|
2 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: genetics.wustl.eduLanguage: English - Date: 2012-08-21 16:02:24
|
|---|
3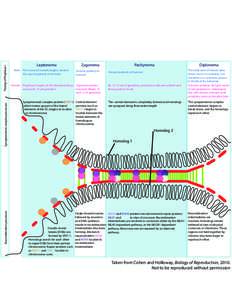 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: meiosis.cornell.eduLanguage: English - Date: 2012-09-13 12:08:14
|
|---|
4 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: www.coopext.colostate.eduLanguage: English - Date: 2013-03-26 15:57:26
|
|---|
5 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: www.biocev.euLanguage: English - Date: 2015-02-27 05:27:57
|
|---|
6 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: www.esp.orgLanguage: English - Date: 2010-05-11 22:25:57
|
|---|
7 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: starlab.comLanguage: English - Date: 2014-02-06 21:17:31
|
|---|
8 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: www.nsta.orgLanguage: English - Date: 2011-06-17 14:51:06
|
|---|
9 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: www.nsta.orgLanguage: English - Date: 2011-03-30 16:00:52
|
|---|
10 | Add to Reading ListSource URL: openwetware.orgLanguage: English - Date: 2014-02-23 10:00:54
|
|---|